
Use a pipe character ( |) to force a line break.Ī chart with a blue, right-aligned, 20-point title.īack to top Chart Legend Text and Style chdl, chdlp, chdls [ All Default is "c".Ī chart with a title, using default color and font size. Choose one of the following case-sensitive string values: "l" (left), "c" (centered) "r" (right). The title color, in RRGGBB hexadecimal format. Use a + sign to indicate spaces,Īnd a pipe character ( | ) to indicate line breaks. You cannot specify where this appears, but youĬan optionally specify the font size and color. You can specify the title text, color, and font size for your chart.Ĭhtt - Specifies the chart title. The rest of the features on this page are standard chart features. The extra lines will cycle through the color list from the beginning. Syntax chco=., Specify one or more line colors in RRGGBB Optionally specify the colors of the lines using the chco parameter. There are two types of radar charts: straight line charts ( cht=r)įor a chart of type r, points are connected with straightĬhart type rs connects points with curved lines. Line shape markers produce a circle on a radar chart. In radar charts, horizontal line markers areīent into circles, and vertical line markers radiate outward from the center, This example uses the same parameters as the previous example, In charts of type rs, points are connected This chart includes x-axis labels that might indicate values at various compass Go from the center of the chart to the top. For radar charts, the x-axis is drawn in a circleĪround the perimeter of the chart, and the y- and r-axes
Line styles are specified with chls, as described in LineĪxis labels are specified with chxt, chxl, and chxr,Īnd labels.
Net radar error chart series#
Of each data series is specified with chco, as described in Series This example is a more complex radar chart with two data series. You can add further information and clarity to a radar chart by adding Notice that the second chart has six segments, which gives seven points to To number of data points, and the second according to the number of labels. The first chart assigns data locations according Number of data points is the same (five), but the first has fewer labels, and Or the number of data points, whichever is larger. Of the data points around the chart is determined by the number of labels, When x-axis labels are included in a radar chart, the spacing Values are gradually increasing, which gives a snail shell appearance. This example shows a simple radar chart, with a single data series. Descriptionįor a chart of type r, points are connected with straight lines. A radar chart can support multiple series. Your data will never go around the chart more than once. More data points will increase the granularity of the chart. N+1 data points to make a complete circuit of the chart, where n is the
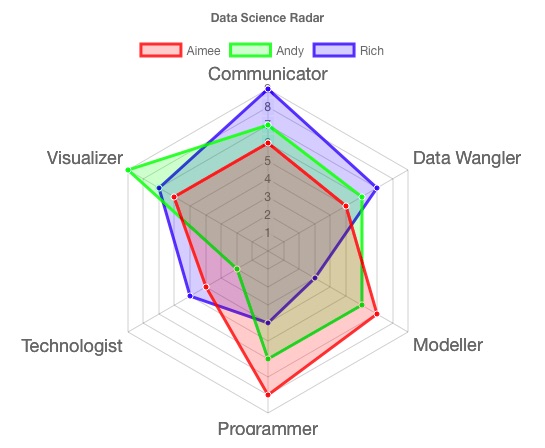
Than four labels or data points, the chart will default to four segments. The minimum number of segments is four if you have fewer If you have multiple series, the series with the So, for instance, if you have a chart with eight data points and no labels, theĭata points will be spaced 45 degrees apart (360 / 8).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
